Light Hydrocarbon
Light Hydrocarbon 1. Definition and Composition “Light hydrocarbon” is a commercial classification for volatile, low-boiling-point fractions derived from crude oil separation processes such as fractionation, blending, and sweetening. These fractions are among the most critical products in the petroleum and petrochemical industries. Fundamentally, hydrocarbons are organic compounds consisting primarily of carbon and hydrogen. The presence…
Heavy Hydrocarbon
Heavy Hydrocarbon 1. Definition and Key Properties “Heavy hydrocarbon” is a commercial classification for mid-distillate refinery products derived from crude oil. These compounds can result from various processes, including blending, fractionation, and sweetening, to meet specific technical specifications. Key physicochemical properties include: Density: > 810 kg/m³ Flash Point: 50–55 °C Molecular Structure: Characterized by large molecules, low volatility,…
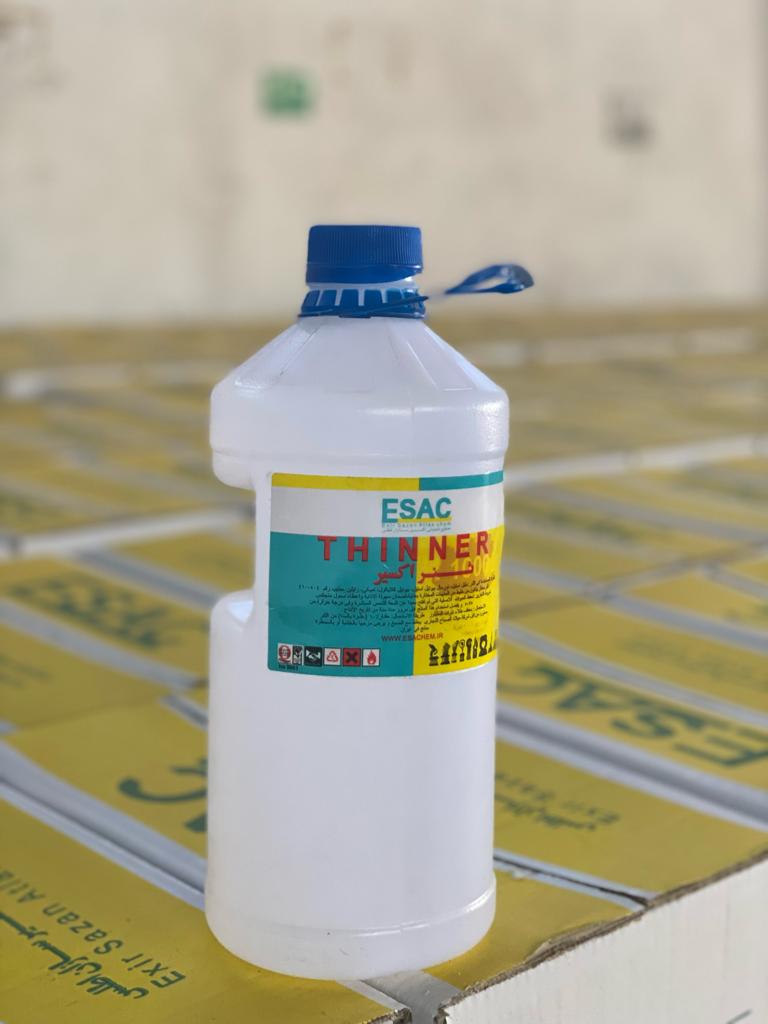
Thinner
Thinner 1. Introduction & Definition Thinners, also known as diluents or solvents, are volatile liquid formulations used to reduce the viscosity of paints and coatings. They are essential for adjusting application properties, controlling drying times, and achieving the desired final film characteristics. An effective thinner dissolves the paint’s resin system, transforming a concentrated product into…
Methanol
Methanol 1. History and Origins The use of methanol dates back to ancient civilizations, including the Egyptians. However, the compound was first isolated in its pure form in 1661 by Robert Boyle, who distilled it from wood. Its elemental composition was identified in 1834 by French chemists Eugène Peligot and Jean-Baptiste Dumas. Originally named “methyl,”…
Naphtha
Naphtha 1. Introduction & CompositionNaphtha is a general term for a group of highly volatile, flammable liquid hydrocarbon mixtures, constituting approximately 15-30% of crude oil. It is a critical feedstock in the petrochemical industry and refers to various refined, partially refined, or unrefined petroleum fractions distilled between 30°C and 240°C, placing it in a similar…
Methyl Acetate
Methyl Acetate Methyl acetate is a neutral, colorless (transparent) liquid belonging to the ester family. This substance is free of volatile organic compounds, is flammable, and has low toxicity; it has an odor similar to glue and acetone. This substance is unstable in strong acidic or basic solutions and is also free of volatile compounds….